Non-Custodial Crypto Swap: The Complete Guide to Safer, Faster Trading
Introduction: What Is a Non-Custodial Crypto Swap?
In the early days of crypto, trading digital assets usually meant sending your coins to a centralized exchange, waiting for deposits to clear, placing an order, then withdrawing back to your wallet. This model works, but it comes with one major drawback: you give up control of your funds, sometimes for hours or days.
A non-custodial crypto swap changes that. Instead of depositing assets into an exchange’s wallet, you trade directly from your own wallet. You stay in control of your private keys, and the platform simply facilitates a swap between one asset and another.
Modern tools make this process extremely simple. For example, you can use a non-custodial swap service to exchange one cryptocurrency for another without creating an account or giving up custody of your assets. This style of trading has quickly become a favorite for users who care about security, privacy, and convenience.
Why Non-Custodial Crypto Swaps Matter
Non-custodial trading isn’t just a technical detail—it fundamentally changes the risk profile of using crypto.
“Not Your Keys, Not Your Coins”
The core principle of cryptocurrency is self-sovereignty: if you control your private keys, you control your funds. Custodial exchanges ask you to override this principle by holding your coins on your behalf. History has shown this can go very wrong:
- Exchange hacks resulting in large fund losses
- Platform insolvency or bankruptcies freezing user assets
- Account closures, freezes, or withdrawal delays
With a non-custodial crypto swap, your assets remain in your wallet until the exact moment they are exchanged. You never hand over control to a third party.
Regulatory and Counterparty Risks
Custodial platforms operate as financial intermediaries. That means they can be affected by:
- Regulatory changes that restrict access to certain users or regions
- Operational failures, internal fraud, or mismanagement of user funds
- Over-leveraging or using customer deposits for other activities
Non-custodial swap tools usually behave more like technical infrastructure than financial custodians. While they are not risk-free, they significantly reduce counterparty exposure because they never hold large pools of user funds.
Privacy and Data Collection
Many centralized exchanges require full KYC (Know Your Customer) verification, including ID uploads, selfies, and personal data. For users who prioritize privacy, that’s a major concern.
By contrast, a non-custodial crypto swap typically allows you to trade directly from your wallet, often without creating a traditional account or sharing extensive personal information. This can help reduce your digital footprint, as long as you use reputable tools and follow security best practices.
Key Benefits of Non-Custodial Crypto Swaps
1. You Keep Control of Your Funds
The most important benefit is straightforward: you retain custody. Your assets stay in your wallet, under your keys, until the moment of the transaction. Even during the swap, many systems are designed so that no single party can unilaterally seize or freeze your funds.
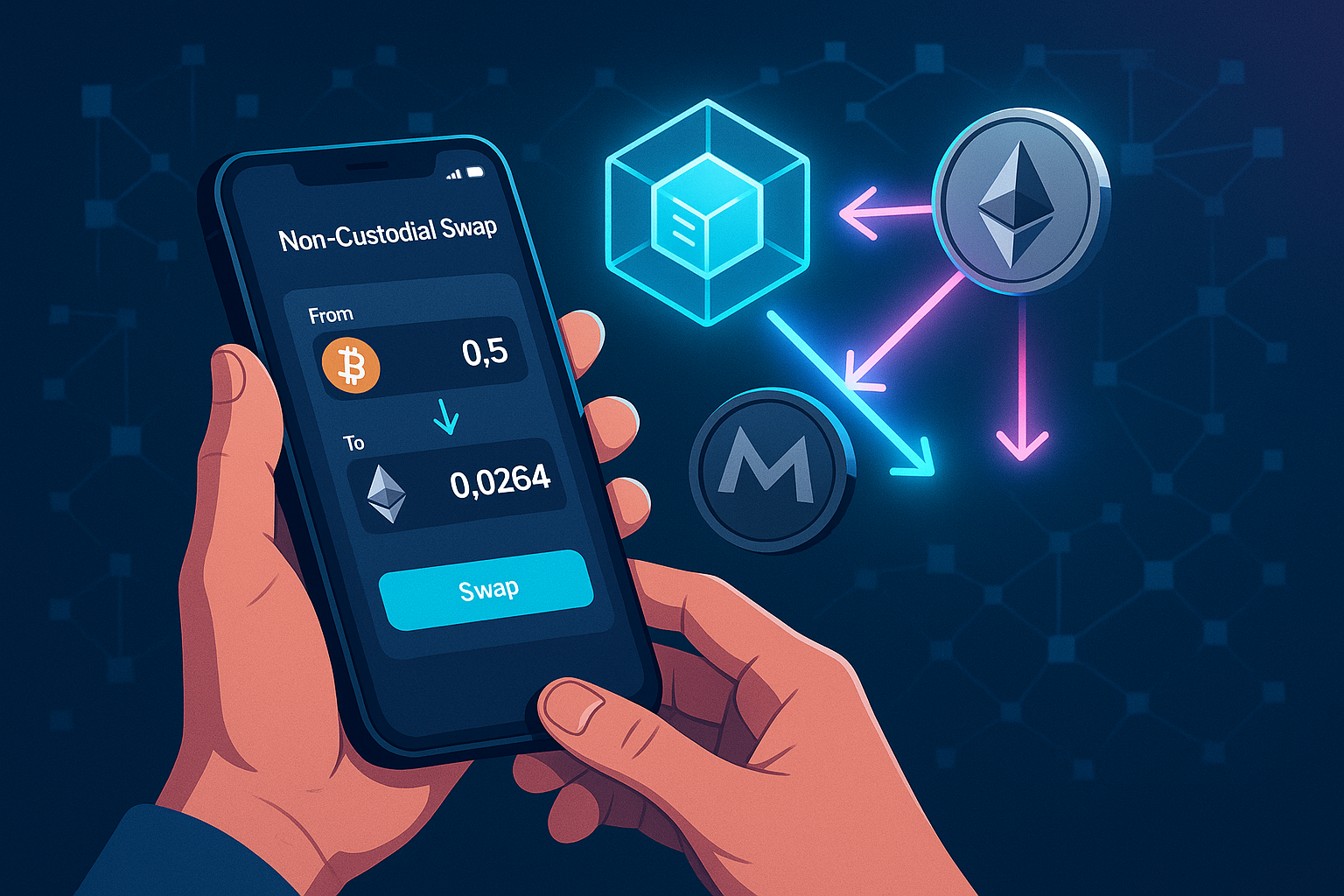

2. Reduced Counterparty Risk
Because non-custodial platforms don’t hold user deposits, they are a much less attractive target for large-scale hacks. While smart contract vulnerabilities or integration risks still exist, you’re no longer exposing all your assets to a centralized honeypot.
3. Often Faster and Simpler
With a good non-custodial interface, you can:
- Connect a wallet (or paste a receive address)
- Select the asset you want to send and receive
- Confirm the transaction in your own wallet
You skip the whole “deposit, wait, trade, withdraw” flow and swap crypto instantly in a single streamlined process.
4. Better Privacy (When Used Properly)
Non-custodial swaps can support a more private trading experience:
- No centralized account balance holding your coins
- Often no extensive KYC for reasonable transaction sizes
- Direct wallet-to-wallet transfers without long-term storage of funds
However, remember that most blockchains are public ledgers. Privacy depends on how you structure your transactions, what networks you use, and whether you reuse addresses.
5. Access to a Wider Range of Assets
Custodial exchanges list only a subset of available tokens, with strict policies and listing fees. Non-custodial protocols and routing tools can often tap into decentralized liquidity across multiple networks and DEXs, allowing access to a broader variety of assets—sometimes including tokens you won’t find on large centralized exchanges.
Risks and Drawbacks You Should Understand
Non-custodial doesn’t mean risk-free. It means the risk profile changes and shifts more responsibility to you.
1. User Error and Self-Custody Responsibility
When you control your keys, you also assume full responsibility for them. Common pitfalls include:
- Sending funds to the wrong address
- Using an incompatible network (e.g., sending ERC-20 tokens to a BTC address)
- Losing your seed phrase or private keys
- Falling for fake websites or phishing links
There is no “support desk” that can reverse a blockchain transaction if you make a mistake.
2. Smart Contract and Protocol Risks
Many non-custodial swap solutions rely on smart contracts or complex routing logic. Risks include:
- Smart contract bugs or security vulnerabilities
- Oracle failures or mispricing events
- Liquidity outages or extreme slippage in volatile markets
Mitigate these by choosing platforms with security audits, established reputations, and transparent documentation.
3. Network Congestion and Fees
Non-custodial swaps typically rely on underlying blockchains like Ethereum, Bitcoin, or others. During times of high network congestion, you may face:
- Higher gas/transaction fees
- Slower confirmation times
- Occasional transaction failures if gas is set too low
Using alternative chains or timing your swaps can help reduce these issues.
4. Limited Support vs. Centralized Exchanges
Custodial exchanges often provide extensive customer support because they manage user accounts and balances. Non-custodial services are more like tools—you’re interacting directly with the blockchain. While some teams have responsive support, they generally can’t “fix” on-chain mistakes, and troubleshooting is more technical.
How a Non-Custodial Crypto Swap Works (Step-by-Step)
Let’s walk through a typical non-custodial swap flow. Details vary by platform, but the general steps are similar.

Step 1: Choose a Reputable Non-Custodial Service
Start by selecting a trustworthy platform that supports the assets and networks you care about. Look for:
- Clear documentation
- Security audits or public security reviews
- Transparent fee structure
- Positive community feedback
Services like GhostSwap’s private exchange interface exemplify the type of non-custodial environment many users prefer: straightforward UX, custodyless design, and a focus on user control.
Step 2: Connect or Specify Your Wallet
Depending on the platform, you’ll either:
- Connect a wallet (e.g., MetaMask, hardware wallet, mobile wallet), or
- Specify a receive address if the flow is more like a one-time “send and receive” process
Make sure you’re connecting the correct wallet and network (e.g., Ethereum mainnet vs. a testnet or an L2).
Step 3: Select the Assets to Swap
Choose:
- The asset and amount you want to send (e.g., 0.1 BTC)
- The asset you want to receive (e.g., ETH, USDT, or another token)
The interface will usually show:
- An estimated rate
- Expected amount received
- Fees and minimum/maximum limits
Step 4: Review the Quote and Terms
Before confirming, check:
- Exchange rate and slippage tolerance
- Network fees (gas or transaction fees)
- Destination address (is it correct and under your control?)
Some services offer fixed-rate quotes for a limited time, while others are fully market-based and can fluctuate slightly until the transaction is mined.
Step 5: Confirm the Transaction from Your Wallet
Once you’re satisfied with the quote:
- Initiate the swap in the interface
- Your wallet will prompt you to confirm the transaction
- Review details one more time, especially the “To” address and network
- Approve the transaction
Your wallet signs and broadcasts the transaction to the blockchain. The non-custodial service monitors the chain, detects your payment, then sends the output asset to the specified receive address.
Step 6: Wait for Confirmations and Verify Receipt
Depending on the network, you may need to wait for a few block confirmations. Once complete:
- Open your wallet and verify the received asset balance
- If necessary, add the token contract address so your wallet shows the new token
- Optionally, check a block explorer to see transaction details
Practical Tips for Using Non-Custodial Crypto Swaps Safely
1. Always Verify the URL
Phishing websites are a major attack vector. Before initiating a swap:
- Type the URL manually or use a trusted bookmark
- Check the domain carefully for misspellings
- Look for HTTPS and a valid certificate (though this alone isn’t enough)
2. Start with Small Test Transactions
When using any new platform or network:
- Begin with a small amount to confirm everything works as expected
- Verify that you receive the right asset on the right network
- Only increase amounts once you’re confident in the process
3. Double-Check Network and Address Compatibility
Common mistakes involve sending funds to:
- The wrong blockchain (e.g., BSC vs. Ethereum)
- An address you don’t actually control
- Exchange deposit addresses incompatible with certain tokens/chains
If you’re sending to an exchange, carefully read their deposit instructions, supported networks, and minimum deposit amounts.
4. Use Hardware Wallets Where Possible
A hardware wallet keeps your private keys offline, dramatically reducing the risk of theft from malware. Many non-custodial swap interfaces integrate with hardware wallets via browser extensions or wallet-connection protocols.
5. Understand Fees and Slippage
Every swap includes some combination of:
- Network fees (gas, BTC transaction fees, etc.)
- Protocol or service fees
- Slippage cost if the market moves during your swap
Review these costs before confirming. In volatile conditions, consider setting stricter slippage limits or waiting for calmer markets.
6. Keep Software and Wallets Updated
Use the latest versions of:
- Your wallet software or extension
- Browser (if applicable)
- Any security tools or plugins
Updates often fix security vulnerabilities and improve compatibility with modern DeFi and swap protocols.
7. Maintain Good OpSec (Operational Security)
Security is not only about the platform—it’s also about your environment:
- Never share your seed phrase or private keys with anyone
- Avoid entering seed phrases into web forms, even “recovery” pages
- Use unique, strong passwords and enable 2FA on related accounts (e.g., email)
- Beware of unsolicited DMs or support impersonators
Who Should Consider Non-Custodial Crypto Swaps?
Non-custodial swaps are especially attractive for:
- Self-custody advocates who don’t want to leave funds on centralized exchanges
- Privacy-conscious users who prefer minimal account creation and data sharing
- Active traders looking for fast, wallet-to-wallet swaps without multiple steps
- Long-term holders who occasionally rebalance their portfolios without parking assets on exchanges
They may be less ideal for users who:
- Need extensive customer support or hand-holding
- Don’t feel comfortable managing private keys
- Primarily trade complex derivatives or margin products (which remain mostly on centralized venues)
Conclusion: The Future Is Non-Custodial
A non-custodial crypto swap offers a powerful combination of control, security, and convenience. Instead of handing assets to an intermediary and hoping for the best, you maintain custody throughout the trading process while still enjoying quick, streamlined exchanges.
As infrastructure matures, more users are recognizing that they don’t have to choose between usability and self-custody. Tools like non-custodial swap platforms show how trading can be both user-friendly and aligned with crypto’s core values of sovereignty and privacy.
If you’re ready to take more control over your digital assets, start by experimenting with small, non-custodial swaps, build your security habits, and gradually incorporate these tools into your regular crypto workflow. Over time, you may find that you rarely need to trust a third-party custodian at all.